Which Process Uses Acetyl Coa as a Reactant
Produces 4 but requires 2 3. Most often used as energy source 4.

Pyruvate Oxidation Biology For Majors I
Electron transport chain ETC Rank of cellular respiration.

. Products of the Krebs cycle include. Carbon skeletons convert to acetyl and enter citric acid cycle 5. Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms.
Reactants and products in glycolysis. For example alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes the. The tests detect the presence of carbon dioxide and ethanol.
Structural biology enzymology and metabolismOver the last decades of the 20th century biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these. Acetyl CoA moves on as the product of pyruvate oxidation to become a reactant in the Krebs cycle. Products of the Krebs cycle include.
During this first step of the citric acid cycle the CoA enzyme which contains a sulfhydryl group -SH is recycled and becomes available to attach another acetyl group. Can produce up to 36 ATP molecules 7. First broken down into glycerol and fatty acids 6.
Fatty acids are converted into acetyl and enter citric acid cycle 3. First broken down into amino acids 8. Carbon dioxide should be present irrespective of.
1 carbon dioxide molecule. Food Chemistry 4th Edition by Belitz W. The citrate will then harvest the.
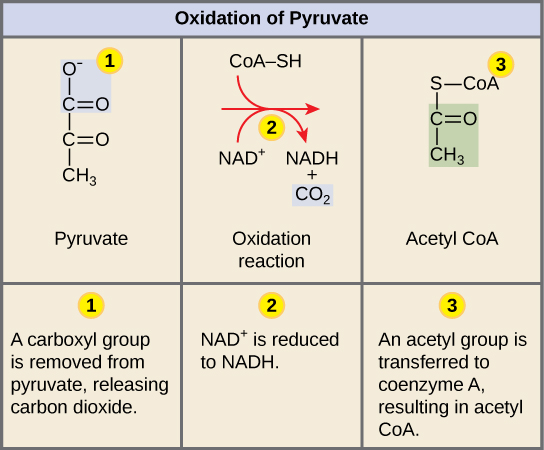
In the process carbon dioxide is released and one molecule of NADH is formed. Upon entering the mitochondrial matrix a multi-enzyme complex converts pyruvate into acetyl CoA. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology biochemistry may be divided into three fields.
A dehydrogenase is an enzyme belonging to the group of oxidoreductases that oxidizes a substrate by reducing an electron acceptor usually NAD NADP or a flavin coenzyme such as FAD or FMNLike all catalysts they catalyze reverse as well as forward reactions and in some cases this has physiological significance. Note that during the second stage of glucose metabolism whenever a carbon atom is removed it is bound to two oxygen atoms producing carbon dioxide one of the major end products of cellular. The citric acid cycle consists of a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of ATP Biology.
In the presence of oxygen acetyl CoA delivers its acetyl group to a four-carbon molecule oxaloacetate to form citrate a six-carbon molecule with three carboxyl groups. Glycerol is converted. In cells of protists plants fungi and animals the Krebs cycle and the ETC take place in organelles called _____ 1.

The Citric Acid Cycle Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy

Oxidation Of Pyruvate And The Citric Acid Cycle Boundless Biology
Pyruvate Oxidation Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy
Comments
Post a Comment